The Clothianidin Chloride Alkalis Insecticide
Chemical name:
1-(2-Chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-2-nitroguanidine
Molecular formula: C6H8ClN5O2S
It's far mainly used as an insecticide for controlling aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, planthoppers and other hemiptera, coleoptera, diptera and positive lepidoptera pests on rice, veggies, fruit bushes and different vegetation.
Usage:
It's far mainly used as an insecticide for controlling aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, planthoppers and other hemiptera, coleoptera, diptera and positive lepidoptera pests on rice, veggies, fruit bushes and different vegetation. it has excessive efficiency, large-spectrum, low dosage, low toxicity, lengthy-lasting efficacy, no harm to vegetation, secure use, no move-resistance to conventional insecticides, and many others. it has outstanding systemic and osmotic consequences and is a substitute for distinctly toxic natural some other variety of phosphorus insecticides. its structure is novel and special, and its performance is better than conventional nicotinic insecticides. it may turn out to be a international huge-scale insecticide species.
Structural formula:
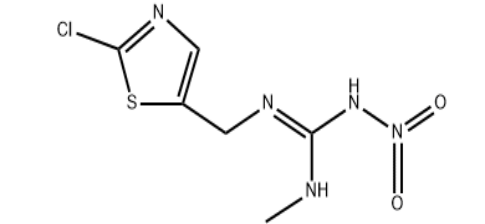
Molecular weight: 249.67
CAS No. : 210880-92-5
Physical and chemical properties:
Physical and chemical properties: The appearance of the original drug is a crystalline solid powder, odorless, with a melting point of 176.8°C.
The appearance of the original drug is a crystalline solid powder, odorless, with a melting point of 176.8°C
Vapor pressure: 1.3×10Pa (25°C).
Solubility: water 0.327g/L, acetone 15.2 g/L, methanol 6.26 g/L, ethyl acetate 2.03 g/L, methylene chloride 1.32 g/L, xylene 0.0128 g/L, n-heptane <0.00104 g/ L, n-octanol 0.938 g/L (measurement temperature: water 25℃, organic solvent 20℃).
Product description:
Clothianidin is an insecticide developed by Takeda Chemical Industries and Bayer AG. Similar to thiamethoxam and imidacloprid, it is a neonicotinoid. Neonicotinoids are a class of insecticides that are chemically similar to nicotine, which has been used as a pesticide since the late 1700s. Clothianidin and other neonicotinoids act on the central nervous system of insects as an agonist of acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter that stimulates nAChR, targeting the same receptor site (AChR) and activating post-synaptic acetylcholine receptors but not inhibiting AChE. Clothianidin and other neonicotinoids were developed to last longer than nicotine, which is more toxic and which breaks down too quickly in the environment. However, studies published in 2012 show that neonicotinoid dust released at planting time may persist in nearby fields for several years and be taken up into non-target plants, which are then foraged by bees and other insects.
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible




