Natural Chlorpyrifos Organophosphorus Insecticide
Chemical name:
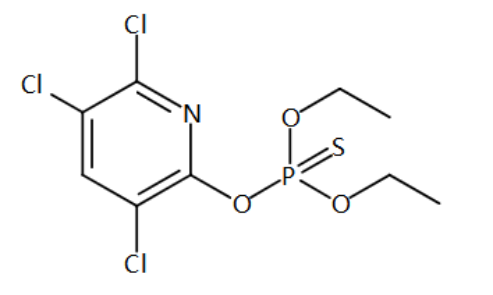
O,O-Diethyl O-(3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl) phosphorothioate
Molecular formula: C9H11Cl3NO3PS
Usage:
Chlorpyrifos is used in approximately one hundred nations round the world to manipulate insects in agricultural, residential, and business settings. its use in residential packages is limited in more than one international locations. in step with dow, chlorpyrifos is registered for use in nearly one hundred nations and is yearly carried out to approximately eight.five million crop acres. the crops with the maximum use consist of cotton, corn, almonds, and fruit trees, consisting of oranges, bananas, and apples. use of chlorpyrifos isn't recommended on tomato crops, because it kills the entire plant inside days.
Chlorpyrifos changed into first registered to be used in the usa in 1965 for manipulate of foliage and soil-born bugs. the chemical have become widely utilized in residential settings, on golfing direction turf, as a structural termite manipulate agent, and in agriculture. most residential use of chlorpyrifos has been phased out inside the u.s.; however, agricultural use stays commonplace.
Structural formula:
Molecular weight: 350.59
CAS No. : 2921-88-2
Product description:
Chlorpyrifos (CPS), also known as Chlorpyrifos ethyl, is an organophosphate pesticide used on crops, animals, and buildings, and in other settings, to kill a number of pests, including insects and worms. It acts on the nervous systems of insects by inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme. Chlorpyrifos was patented in 1966 by Dow Chemical Company.
Chlorpyrifos is considered moderately hazardous to humans by the World Health Organization based on its acute toxicity. Exposure surpassing recommended levels has been linked to neurological effects, persistent developmental disorders, and autoimmune disorders. Exposure during pregnancy may harm the mental development of children, and most home uses of chlorpyrifos were banned in the U.S. in 2001. In agriculture, it is "one of the most widely used organophosphate insecticides" in the United States, and before being phased out for residential use it was one of the most used residential insecticides.
Physical and chemical properties:
white crystals, with a slight thiol smell
Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.398
Melting point (℃): 42.5-43
Boiling point (℃, normal pressure): 200
Refractive index: 1.56
Flash point (℃): 181.1
Water solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents
Submitted successfully
We will contact you as soon as possible




